
Part 2: Configure IPv6 Addressing on the Servers Step 1: Configure IPv6 addressing on the Accounting Server. Configure the IPv6 address, the link-local and activate the interface.Enter the commands necessary to transition to interface configuration mode for Serial0/0/0.Step 4: Configure IPv6 addressing on Serial0/0/0. Configure the IPv6 address, the link-local address and activate the interface.Refer to the Addressing Table to obtain the correct IPv6 address.Enter the commands necessary to transition to interface configuration mode for GigabitEthernet0/1.Step 3: Configure IPv6 addressing on GigabitEthernet0/1. R1(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local.Configure the link-local IPv6 address with the following command:.Configure the IPv6 address with the following command:.Enter the commands necessary to transition to interface configuration mode for GigabitEthernet0/0.Step 2: Configure IPv6 addressing on GigabitEthernet0/0. This command will be discussed in a later semester. This command must be configured to enable the router to forward IPv6 packets.
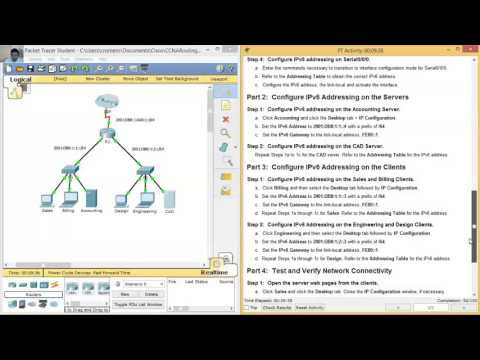
Enter the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command.Part 1: Configure IPv6 Addressing on the Router Step 1: Enable the router to forward IPv6 packets. You will also practice verifying your IPv6 addressing implementation. In this activity, you will practice configuring IPv6 addresses on a router, servers, and clients. Part 4: Test and Verify Network Connectivity Background Part 3: Configure IPv6 Addressing on Clients Part 2: Configure IPv6 Addressing on Servers Part 1: Configure IPv6 Addressing on the Router In this way, a network packet is similar to a package being delivered in the mail, with user data representing the content inside the package and control information as the delivery instructions found on it.7.2.4.9 Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv6 Addressing Addressing Table Device Control information, on the other hand, comprises instructions required for the content to reach its destination-including source and destination IP addresses, error codes, etc. Each packet contains both user data and control information. When one computer needs to send information to another over a network, the data is divided into a series of packets-small bits of the original data. In this post we shed some light on the GRE protocol: how it works, what it is capable of and how it can be effectively utilized. GRE protocol offers a number of advantages, including: Use of multiple protocols over a single-protocol backbone Providing workarounds for networks with limited hops Connection of non-contiguous subnetworks Being less resource demanding than its alternatives e. Download Lab Here Generic routing encapsulation GRE is a communication protocol used to establish a direct, point-to-point connection between network nodes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
